How Many People Register To Be Democrat

Map of the Commune of Columbia, states, and territories in the United States that crave voter registration to vote:
Voter registration required for federal and state elections
No voter registration required for federal or state elections, except some local city elections require voter registration

A grouping of African American children get together around a sign and berth to register voters. Early on 1960s.
Voter registration in the United states of america is required for voting in federal, land and local elections in the Usa. The only exception is North Dakota, although cities in Due north Dakota may register voters for city elections.[1] Voter registration takes place at the county level in many states and at the municipal level in several states. Most states set cutoff dates for voter registration and to update details, ranging from two to iv weeks before an election; while a third of states take Election Twenty-four hours or "same-day" voter registration which enables eligible citizens to annals or update their registration when they vote before or on ballot day.
It has been argued that some registration requirements deter some people (peculiarly disadvantaged people) from registering and therefore exercising their right to vote, resulting in a lower voter turnout. Several consequences of registering for voting are mentioned sometimes every bit deterrents for registration, similar to serve jury duty, to be drafted into the military, or to update auto insurance in case of changing accost of residence, for example. Just many of these claims are false or, similar being listed every bit potential juror, are merely applicative to sure jurisdictions or are not the but way to exist called in to serve.[2]
Co-ordinate to a 2012 report, 24% of the voting-eligible population in the The states are not registered to vote, equaling some 51 meg U.S. citizens.[three] [4] While voters traditionally had to register at authorities offices by a sure period of fourth dimension before an election, in the mid-1990s, the federal regime fabricated efforts to facilitate registering, in an effort to increase turnout. The National Voter Registration Act of 1993 (the "Motor Voter" constabulary) now requires state governments to either provide uniform opt-in registration services through drivers' license registration centers, disability centers, schools, libraries, and mail-in registration, or to let Election Day voter registration, where voters can register at polling places immediately prior to voting. In 2016, Oregon became the outset land to make voter registration fully automatic (opt-out) when issuing driver licenses and ID cards, since followed past 15 more states and the Commune of Columbia. Political parties and other organizations sometimes concur "voter registration drives", that is, events to register new voters.
In 31 states and the District of Columbia, persons registering to vote may at the same time declare an affiliation with a political party.[5]
History [edit]
In 1800, Massachusetts was the first state to require voter registration equally a prerequisite for voting statewide,[6] which was followed past Maine (1821), Pennsylvania (1836) and Connecticut (1839). During the 19th century, and especially after the Civil State of war, more than states and cities would establish voter registration as a prerequisite to voting, partially to prevent voting past immigrants in cities. However, it was non until 1913 when Nebraska became the first land to establish a permanent statewide voter register, overseen by an ballot commissioner.
According to a 2020 report, voter registration laws adopted in the menstruation 1880–1916 reduced turnout as much as xix percentage points.[7]
North Dakota abolished voter registration in 1951 for land and federal elections, the only country to do so.[1] It has since 2004 required voters to produce ID at time of casting a vote. This has led to North Dakota being accused of voter suppression considering many Native American were denied a vote considering the address on their tribal IDs had a postal service office box accost, which continues to exist a mutual practice.[eight]
In 2002, Arizona made online voter registration available. In 2016, Oregon became the start land to implement a fully automatic (opt-out) voter registration system tied to the process of issuing commuter licenses and ID cards.
No registration jurisdiction [edit]
North Dakota is the only state that does not take voter registration, which was abolished in 1951, although cities in North Dakota may register voters for urban center elections.[1] [9] In North Dakota voters must provide identification and proof of entitlement to vote at the polling place before being permitted to vote.
Due north Dakota is exempt from the requirements of the federal National Voter Registration Deed of 1993. Because of this exemption, North Dakota has since 2004 required voters to produce an approved class of ID earlier existence able to vote, i of which was a tribe ID commonly used by Native Americans. It was common and lawful for a mail office box to be used on this ID, instead of a residential address, considering there are no street addresses on reservations. In 2016, a change required tribal ID to have a residential address to be accepted, and North Dakota has been accused of voter suppression with many Native Americans being denied a vote because they did not have an approved grade of ID with a residential address.[x]
North Dakota's ID law especially adversely affected large numbers of Native Americans, with almost a quarter of Native Americans in the land, otherwise eligible to vote, being denied a vote on the ground that they do not accept proper ID; compared to 12% of non-Indians. A gauge overturned the ID police in July 2016, also proverb: "The undisputed evidence earlier the Court reveals that voter fraud in North Dakota has been virtually non-real."[11] Nevertheless, the deprival of a vote on this basis was also an upshot in the 2018 mid-term election.[10]
Federal jurisdiction [edit]
While the United states of america Congress has jurisdiction over laws applying to federal elections, it has deferred well-nigh aspects of election police to the states. The Us Constitution prohibits states from restricting voting rights in ways that borrow on a person'southward right to equal protection nether the law (14th Amendment), on the ground of race (15th Subpoena), on the basis of sex activity (19th Amendment), on the basis of having failed to pay a poll tax or any tax (24th Amendment), or on the basis of age for persons historic period 18 and older (26th Subpoena). The administration of elections, nonetheless, vary widely across jurisdictions.
In general, US citizens over the age of 18 accept the right to vote in federal elections.[12] In a few cases, permanent residents ("greenish card" holders) have registered to vote and have cast ballots without realizing that doing so was illegal. Non-citizens convicted in criminal court of having made a simulated merits of citizenship for the purpose of registering to vote in a federal ballot can be fined and imprisoned for up to a twelvemonth. Deportation and removal proceedings take resulted from several such cases.[13] Some municipalities allow non-citizen residents to vote in municipal or schoolhouse commune elections.
All states except Maine and Vermont (and the Commune of Columbia) deny the vote to bedevilled felons for some duration, a exercise known equally felony disenfranchisement. In 16 states, voting is only prohibited during incarceration. 21 states additionally prohibit voting during parole or probation but allow voting after. Xi states either indefinitely append voting rights or require special action to have voting rights restored.[fourteen]
Effect on participation [edit]

A 2012 study past The Pew Charitable Trusts estimates that 24% of the voting-eligible population in the The states are non registered to vote, a percentage that represents "at least 51 million eligible U.S. citizens."[fifteen] [xvi] The written report suggests that registration requirements contribute to discouraging people from exercising their correct to vote, thereby causing a lower voter turnout. The extent of discouragement and its effect on increasing the socioeconomic bias of the electorate however remain contested.
In a 1980 landmark study, Raymond East. Wolfinger and Steven J. Rosenstone came to the decision that less restrictive registration requirements would substantially increase the electoral turnout. According to their probit analysis, if all states adopted the procedures of the most permissive land regulations, which would mean:
- eliminating the closing engagement
- opening registration offices during the xl-hr piece of work calendar week
- opening registration offices in the evening or on Sat
- permitting absentee registration for the ill, disabled and absent
(p 73) turnout in the 1972 presidential election would accept been 9.1% college, with 12.2 1000000 additional people having voted.[17] In a seminal 1988 book, sociologists Richard Cloward and Francis Fox Piven argued that lowering registration requirements would improve socioeconomic equality in the composition of the electorate.[xviii]
Findings such as this have inspired lawmakers to facilitate the registration process, eventually leading to the National Voter Registration Act of 1993 (or "Motor Voter" act) that required states to allow voter registration at various public offices, including drivers' license registration centers, disability centers, schools, libraries, equally well as mail-in registration, unless a state adopts Election Day voter registration. The manner towards passing this piece of federal legislation was notwithstanding lengthy and rocky, every bit these reforms were highly contested. In an expanded 1990 edition of their 1988 volume, titled "Why Americans still don't vote: and why politicians desire information technology that way," Cloward and Piven argued that the reforms were expected to encourage less-privileged groups which happen to lean towards the Democratic Party.[nineteen]
While the turnout at federal elections did substantially increment following the balloter reforms, the issue fell short of Wolfinger and Rosenstone's expectations while Cloward's and Piven's hope of improving the demographic representativeness of the electorate wasn't fulfilled at all. Political scientist Adam Berinsky concluded in a 2005 article that the reforms designed to brand voting "easier" in their entirety had an opposite issue, actually increasing the preexisting socioeconomic biases by ensuring "that those citizens who are virtually engaged with the political globe – those with politically relevant resources – go on to participate, whereas those individuals without such resources autumn by the wayside."[20] Every bit Berinsky reaffirms in a 2016 slice, the only way to increase turnout while improving representativeness is making more than people become interested in politics.[21]
Registration centers [edit]
Traditionally, voter registration took place at government offices, just the federal National Voter Registration Act of 1993, which came into event on January 1, 1995, simplified registration. The Act requires state governments to provide opt-in registration services through drivers' license registration centers, disability centers, schools, libraries, as well as providing for mail-in registration. However, six states are exempt from the streamlined processes under the Human activity: North Dakota, Idaho, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Wisconsin and Wyoming.
Online Registration [edit]
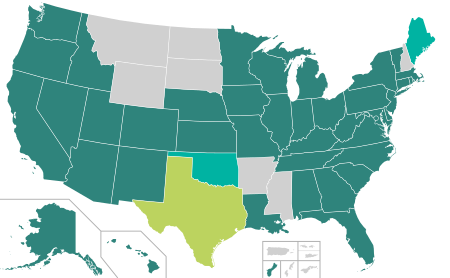
States, territories and the District of Columbia, that allow online voter registration:
Online voter registration available[a]
Online voter registration allowed for those updating their driver'southward license or state IDs
Online voter registration to be implemented
Online voter registration legislation passed at least 1 chamber.
No online voter registration available
Every bit of August 2020, online voter registration was bachelor in 41 states, the District of Columbia, and Guam, with two additional states (Maine and Oklahoma) phasing in implementation.[22] North Dakota does non have voter registration. Since a federal judicial order in September 2020, Texas allows residents to register to vote online if and when they are renewing their commuter's licenses or state identification cards.[23]
| Country or federal district | Date online voter registration implemented | Website |
|---|---|---|
| | 2016-12-01[24] | Alabama Votes |
| | 2015-eleven[25] | Alaska Online Voter Registration |
| | 2002-07[26] | Service Arizona Voter Registration |
| | 2012-09-19[27] | California Online Voter Registration |
| | 2010-04-01[28] | Become Vote Colorado |
| | 2014-01-01[29] | Connecticut Online Voter Registration |
| | 2014-04[22] | I Vote Delaware |
| | 2015[25] | Commune of Columbia Online Voter Registration |
| | 2017-10-01[22] | Register to Vote Florida Voter Registration |
| | 2014-03[25] | Georgia Online Voter Registration |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] | Guam Online Voter Registration |
| | 2015-08-04[30] | Hawaii Online Voter Registration |
| | 2017-12-06[31] | Idaho Votes |
| | 2014-06-17[32] | Illinois Online Voter Registration |
| | 2010-07-01[33] | Indiana Online Voter Registration |
| | 2016-01-04[34] | Iowa Online Voter Registration |
| | 2009-05[25] | Kansas Online Voter Registration |
| | 2016-03-01[35] | Kentucky Online Voter Registration |
| | 2010-04[25] | Geaux Vote |
| | 2023-11 [36] | Due north/A |
| | 2012-07-01[37] | Maryland Online Voter Registration |
| | 2015-06-23[38] | Massachusetts Online Voter Registration |
| | 2019-12-02[39] | Michigan Online Voter Registration |
| | 2013-09-26[xl] | MN Votes |
| | 2014[22] | Vote Missouri |
| | 2015-09-22[41] | Nebraska Online Voter Registration |
| | 2012-09[25] | Nevada Online Voter Registration |
| | 2020-09-04[42] [43] | New Jersey Online Voter Registration |
| | 2016-01-01[44] | New Mexico Online Voter Registration |
| | 2011[22] | New York Electronic Voter Registration |
| | 2020-03-20 | North Carolina Online Voter Registration |
| | 2017-01-01[46] | Ohio Online Voter Registration |
| | 2020[47] | Not fully implemented yet[47] [d] |
| | 2010-03-01[48] | OreStar |
| | 2015-08-27[49] | PA Online Voter Registration |
| | 2016-08-01[50] | RI Online Voter Registration |
| | 2012-x-02[51] | Due south.C. Online Voter Registration |
| | 2017-08-29[52] | GoVote TN Voter Registration |
| | 2020-09[23] | Northward/A[e] |
| | 2010-06[25] | Utah Online Voter Registration |
| | 2015-10-12[53] | Vermont Online Voter Registration |
| | 2013-07-23[54] | Virginia Voter Registration |
| | 2008-01[25] | MyVote |
| | 2015-09[25] | West Virginia Online Voter Registration |
| | 2017-01-09[55] | My Vote Wisconsin |
- ^ In Missouri, a person can register to vote online and electronically provide a signature using a mobile device, tablet computer or touchscreen figurer, but not a standard desktop estimator. The state reviews the information and prints out the registration form, which it sends to the person's local elections part for verification.
- ^ In Missouri, a person tin can register to vote online and electronically provide a signature using a mobile device, tablet calculator or touchscreen computer, but not a standard desktop estimator. The country reviews the information and prints out the registration form, which it sends to the person's local elections office for verification.
- ^ Prior to March 30, 2020, applicants could but apply online as an actress pick in the process of conducting a separate transaction through the Due north Carolina Department of Motor Vehicles. In response to the closure of most DMV offices due to COVID-19, the NCDMV opened online voter registration for all holders of North Carolina driver's licenses and state ID cards and removed the need for a transaction.
- ^ In Oklahoma, registered voters can update their registration data online just new voters and voters who have inverse names or moved to a different county must fill out a paper class.
- ^ Since a federal judicial club in September 2020, Texas allows residents to annals to vote online if and when they are renewing their commuter'southward licenses or state identification cards. Voters with neither card must register by newspaper.
Automated voter registration [edit]

Map of the Commune of Columbia, states, and territories in the The states that let automated voter registration:
Automatic voter registration bachelor
Automatic voter registration to exist implemented
No automated voter registration available
Every bit of July 2019, 16 states and the Commune of Columbia had automatic registration of citizens who interact with country agencies such as the DMV, along with 7 other states that have passed legislation or committed administratively to create automatic registration systems, but not yet implemented it.[56] [57] [58] Those interacting with the land agencies take the choice to opt-out of registering.
On January ane, 2016, the Oregon Motor Voter Deed implemented automatic voter registration of eligible citizens tied to the process of issuing driver licenses and ID cards, with the person having the right to opt out.[59] By April 2016 three more than states – California, West Virginia, and Vermont – adopted the system, and in May 2016 Connecticut announced plans to implement it administratively rather than by legislation.[threescore] [61] Alaskan voters approved Measure 1 on Nov 8, 2016, to allow residents to register to vote when applying annually for the country's Permanent Dividend Fund.[62] [63] Voter approval of Measure 1 fabricated Alaska the first country to implement automated (opt-in) voter registration via ballot initiative. New York passed automatic voter registration on Dec 22, 2020, with implementation to commence in 2023.[64] Several more states take considered legislation for automated registration.[65] On August 28, 2017, Illinois set July i, 2018, for implementation of automatic voter registration at motor vehicle agencies, and a yr later at other state agencies.[66]
| State or federal district | Automatic voter registration implemented |
|---|---|
| | 2017-03-01[67] |
| | 2017-04[58] |
| | 2017-02[58] |
| | 2018 |
| | 2023[68] [69] |
| | 2018-06-26[seventy] |
| | 2016-09[58] |
| | 2018-07-02[71] |
| | 2022-01[72] [73] |
| | 2019-07-01[58] |
| | 2020-01[58] |
| | 2019-09-09[74] |
| | 2020-01[75] |
| | 2018-11-01[76] [58] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [77] |
| | 2020-12-22[78] |
| | 2016-01-01[79] |
| | 2018-06[58] |
| | 2017-01[58] |
| | 2020-04[80] |
| | 2019-07[58] |
| | 2019-07[58] |
Fractional Automatic [edit]
This type does transfer some data from DMV electronically to election officials. For instance, name, age and address. However, does not fully meet the definition of an fully automated organization, considering it is yet relying on newspaper forms in some manner.[81]
Ballot 24-hour interval / same-day [edit]

Map of the District of Columbia, states, and territories in the United States that allow same-twenty-four hour period voter registration:
Same-day and early voting menstruation voter registration available
Same-solar day voter registration bachelor[a]
Early on voting period voter registration available
Same-twenty-four hour period and early voting period voter registration not implemented yet
No same-twenty-four hours and early voting flow voter registration bachelor
The majority of states require voters to register two to iv weeks before an election, with cutoff dates varying from 30 to 15 days.
Some states allow Election Day voter registration (also known every bit EDR) which enables eligible citizens to register to vote or update their registration when they arrive to vote. Some states call the procedure same-day registration (SDR) considering voters can register and vote during the early voting menstruum before Election Day.
EDR allows eligible citizens to annals or update their registration at the polls or their local election office past showing valid identification to a poll worker or ballot official, who checks the identification, consults the registration list and, if they are not registered or the registration is out of engagement, registers them on the spot.
As of March 27, 2018, 17 states and the District of Columbia offer same day voter registration, which allows any qualified resident of the state to become to register to vote and cast a election all in that day. Additionally, 1 state (Washington) has enacted aforementioned day vote registration, which has all the same to be implemented.[82] Also, 9 states have voter registration possible for a portion of their early voting periods.
5 states are exempt from the National Voter Registration Act of 1993 because they have continuously since 1993 had EDR: Idaho, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Wisconsin and Wyoming. Maine lost the exemption when it abolished EDR in 2011, though it was restored later that year. North Dakota is besides exempt considering it does not have voter registration. In June 2011, Maine abolished EDR, which had been in place since 1973, and abolished absentee voting during the ii business concern days earlier an election.[83] However, the stipulation banning EDR was overturned in a November 2011 citizen referendum ("people'south veto") titled Question ane,[84] when Maine voters reinstated EDR with 59% in favor.[85]
Voter turnout is much higher in states using EDR than in states that practise not. A 2013 report analyzing turnout in the 2012 United States presidential election, had SDR states averaging at a turnout of 71%, well in a higher place the average voter turn-out rate of 59% for non-SDR states.[86] Co-ordinate to official turnout data study in the 2014 edition of America Goes to the Polls,[87] voter turnout in EDR states has averaged 10–fourteen percent higher than states that lack that option.[88] Other enquiry suggests that EDR increases turnout between three and xiv per centum points.[89] [90] [91] [92] [93] A 2004 written report summarizes the affect of EDR on voter turnout as "near v percent points".[94] A 2021 study establish that aforementioned twenty-four hours voter registration disproportionately increase turnout among immature voters; young voters move more than ofttimes, which disproportionately burdens them nether traditional voter registration laws.[95]
| Federal district or country | Same day voting registration implemented | Early voting menstruum registration implemented |
|---|---|---|
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | Due north/A[82] |
| | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | Due north/A[82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [b] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | 1973 [96] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | Due north/A[82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | 2019[97] [82] | 2019[97] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] | North/A[82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [77] [98] [82] | [ information unknown/missing ] [77] [98] [82] |
| | N/A[82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] |
| | 2019[82] | 2019[82] |
| | [ data unknown/missing ] [82] | N/A[82] |
| | [ information unknown/missing ] [82] | Due north/A[82] |
- ^ In Illinois, you can annals 27 days before though election twenty-four hour period
- ^ In Illinois, you tin can annals 27 days before though election day
Permanent & portable registration [edit]

Map of the District of Columbia, states, and territories in the United states of america that allow permanent & portable voter registration:
Permanent & portable voter registration available for registered voter
Permanent & portable voter registration available for registered voters who move to a precinct that has an electronic poll book or are an active military member
Conditional ballots available for registered voters who move
No permanent & portable registration available
As of 2014, Delaware, Hawaii, Oregon, and Texas let registered voters who accept moved within the country to update their registrations when they vote, and are given a regular ballot when they vote. Florida requires whatever registered voter who moved to another county and another voting precinct to vote only past a provisional ballot, except if "the precinct to which you have moved has an electronic poll book or y'all are an agile armed services member", in which case the voter would be given a regular ballot when they vote. As of 2014, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Ohio, and Utah allow registered voters who have moved within the state or the District of Columbia to vote in their new canton without re-registering at their new address, but they can only vote a provisional ballot, which could crave further activeness from the voter before information technology is counted.[99] [100]
Preregistration [edit]

Map of the District of Columbia, states, and territories in the United states that allow preregistration prior to turning xviii years old:
Preregistration after turning 16 years old
Preregistration after turning 17 years quondam
Preregistration prior to turning eighteen years old
No preregistration; tin only vote afterward turning xviii years former
Unknown
Preregistration allows individuals younger than 18 years of age to register to vote, but non to actually vote until they accomplish 18. All states take some form of preregistration, starting at age sixteen, except for Northward Dakota which does not have whatsoever registration.[101]
| Federal commune of state | Preregistration requirements |
|---|---|
| | 18 years quondam by the ballot date[101] |
| | Within 90 days preceding 18th birthday[101] |
| | eighteen years onetime by the ballot date[101] |
| | 18 years one-time by the election engagement[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | eighteen years old past the election date[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | sixteen-yr-olds may preregister[101] |
| | xvi-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 17.5-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister, and 17-year-olds may register merely not vote[101] |
| | 18 years erstwhile past the election date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the ballot date[101] |
| | 18 years old past the ballot date[101] |
| | 17.5-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election date[101] |
| | xviii years one-time by the election date[101] |
| | 16-twelvemonth-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 17-twelvemonth-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old past the election date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election date[101] |
| | xviii years old by the election engagement[101] |
| | 17.5-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the ballot date[101] |
| | 17-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years erstwhile by the election appointment[101] |
| | 17-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election date[101] |
| | 16 twelvemonth olds may preregister[101] |
| | sixteen-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | xviii-year-olds past the election date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election date[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old past the election engagement[101] |
| | 16-year-olds may preregister, and 17-year-olds may register if they volition exist 18 years old past the ballot[101] |
| | eighteen years old past the election date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election engagement[101] |
| | 18 years quondam by the election date[101] |
| | Individuals 17 years and 10 months old may register |
| | xvi-year-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old by the ballot date[101] |
| | xviii years erstwhile past the election date[101] |
| | 18 years quondam by the election engagement[101] |
| | 17-yr-olds may preregister[101] |
| | 18 years old by the ballot date[101] |
| | 18 years old by the election appointment[101] |
Registration Drives [edit]

A voter registration bulldoze is an endeavor undertaken by a government authority, political party or other entity to register to vote persons otherwise entitled to vote. In many jurisdictions, the functions of electoral authorities includes endeavours to go equally many people to register to vote as possible. In about jurisdictions, registration is a prerequisite to a person being able to vote at an election.
In the United States, such drives are often undertaken past a political campaign, political party, or other exterior groups (partisan and non-partisan), that seeks to register persons who are eligible to vote but are not registered. In all U.Due south. states except Northward Dakota, registration is a prerequisite to a person being able to vote at federal, state or local elections, as well as to serve on juries and perform other civil duties. Sometimes these drives are undertaken for partisan purposes, and target specific demographic groups considered to exist likely to vote for one candidate or other; on the other hand, such drives may be undertaken by non-partisan groups and targeted more than generally.
In 2004, the Nu Mu Lambda chapter of Alpha Phi Blastoff fraternity held a voter registration drive in DeKalb Canton, Georgia, from which Georgia Secretary of Land Cathy Cox (Dem.) rejected all 63 voter registration applications because the fraternity did not obtain specific pre-clearance from the state to conduct their drive. Nu Mu Lambda filed Charles H. Wesley Education Foundation five. Cathy Cox (Wesley five. Cox)[102] asserting that the Georgia'south long-standing policy and practice of rejecting mail-in voter registration applications that were submitted in bundles, by persons other than registrars, deputy registrars, or "authorized persons", violated the requirements of the National Voter Registration Act of 1993 by undermining voter registration drives. A senior U.S. District Judge upheld earlier federal court decisions in the example, which found that private entities have a right, nether the federal law, to engage in organized voter registration action in Georgia at times and locations of their choosing, without the presence or permission of state or local election officials.[103]
National organizations that regularly piece of work to register voters and promote citizens' appointment in elections include:
- Advancement Project
- Close Up Foundation
- Democrats Abroad
- HeadCount
- League of Women Voters
- Let America Vote
- National Clan for the Advancement of Colored People
- Nonprofit VOTE
- Our Time
- Rock the Vote
- Southern Regional Quango
- Southwest Voter Registration Pedagogy Project
- Educatee Association for Voter Empowerment
- The Voter Participation Center
- U.S. Vote Foundation
- United States Hispanic Chamber of Commerce
- Vote.org
- Voto Latino
Party affiliation [edit]
In 31 states and the District of Columbia, voters are allowed to marking their party affiliation, or their unaffiliated condition, on their voter registration course. In those states which host closed primaries for political parties, voters are often mandated to declare their party affiliation prior to receiving a main election, whether on the 24-hour interval of the main or past a prior deadline.[five] In addition, voters who are party-affiliated in their voter files are about often immune to participate in intra-party elections and decision-making.
Youth Voting [edit]
In some cities, people younger than 18 can vote in local elections, such every bit for city councils and school boards. Takoma Park, Maryland, was the get-go city to allow youth voting, starting in 2013. Other nearby cities, including Hyattsville, Greenbelt and Riverdale Park adopted similar measures.[104] Washington, DC'south city council considered a bill that would expand youth voting in 2018, allow residents sixteen or older to cast ballots in all elections, including federal elections.[105]
Borderline to re-register with a political party for a primary ballot [edit]
| Federal district of land | Deadline to re-register with a political party for a partisan principal election | Deadline to re-register with a political party for the 2020 U.S. Presidential Caucuses and Primary elections |
|---|---|---|
| | 29th twenty-four hour period prior to the partisan primary election[106] | 2020-02-03[106] |
| | 3 months prior to the partisan principal election[107] | [ data unknown/missing ] [108] |
| | The last Saturday in May of the year of the partisan main election | [ data unknown/missing ] [109] |
| | 21st twenty-four hour period prior to the partisan main election[110] | [ data unknown/missing ] [110] |
| | 10th Friday prior to the partisan primary ballot[111] [a] | [ data unknown/missing ] [112] |
| | 14th day prior to the partisan chief election[113] [b] | [ data unknown/missing ] [114] |
| | Dec 31 of the yr prior to the partisan primary election[115] | [ data unknown/missing ] [115] |
| | 15th day prior to the partisan primary election[113] [c] | [ information unknown/missing ] [116] |
| | 1st Tuesday of June of the year of the partisan primary election[117] [d] | [ data unknown/missing ] [118] |
| | 55th twenty-four hours prior to the partisan primary election[113] [e] | 2020-04-08[119] |
| | The Friday ten weeks earlier the Presidential Chief Election in 2020 [120] | 2020-02-14[121] |
| | 30th day prior to the partisan master election[122] | [ data unknown/missing ] [123] |
| | 14th day prior to the partisan primary election[124] | [ data unknown/missing ] [124] |
- ^ In Idaho, unaffiliated registered voters may re-register up to and on the partisan primary twenty-four hours
- ^ In Kansas, unaffiliated registered voters may re-register up to and on the partisan primary solar day
- ^ In Maine, unenrolled registered voters may re-annals upward to and on the partisan principal day
- ^ In New Hampshire, unafflicted registered voters may re-register up to and on the partisan chief solar day
- ^ In New Jersey, unaffiliated registered voters may re-register up to and on the partisan primary solar day
Run across too [edit]
- Voter ID laws in the United States
Further reading [edit]
- Alexander Keyssar. 2009. The Correct to Vote: The Contested History of Democracy in the United States. Basic Books.
- Jimmy Carter Tried to Brand Information technology Easier to Vote in 1977. The Right Stopped Him With the Same Arguments It'south Using Today (Excerpt from Reaganland: America'due south Right Plow 1976-1980 by Rick Perlstein
References [edit]
- ^ a b c "The Voter'south Self Defense Arrangement". Vote Smart . Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ The Well-nigh Common Myths About Voter Registration, Debunked, https://lifehacker.com/the-most-mutual-myths-almost-voter-registration-debunke-1829497517
- ^ "Inaccurate, Costly, and Inefficient: Bear witness That America'south Voter Registration Arrangement Needs an Upgrade" (PDF). The Pew Charitable Trusts. Feb 2012. Retrieved Feb xvi, 2015.
- ^ "Make Information technology Easy: The Case for Automatic Registration". Commonwealth. 2013. Retrieved February 16, 2015.
- ^ a b Cook, Rhodes. "Registering By Party: Where the Democrats and Republicans Are Ahead – Sabato's Crystal Ball". Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December five, 2020. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived re-create every bit title (link) - ^ Perez, Vanessa M. (Feb 1, 2021). "America'due south first voter identification laws: The furnishings of personal registration and declining party competition on presidential election turnout, 1880–1916". Electoral Studies. 69: 102263. doi:10.1016/j.electstud.2020.102263. ISSN 0261-3794.
- ^ North Dakota, native tribes concord to settle voter ID lawsuit to combat voter suppression
- ^ Secretary of State N Dakota. "Voter Registration in North Dakota". Retrieved August 4, 2010.
- ^ a b NBC News. North Dakota, native tribes agree to settle voter ID lawsuit to combat voter suppression. Feb xiv, 2020.
- ^ "Equally November Approaches, Courts Deal Series Of Blows To Voter ID Laws". NPR. August 2, 2016.
- ^ "The Right to Vote". United States Citizenship and Clearing Services. Archived from the original on October 17, 2011. Retrieved October 25, 2011.
- ^ Kirk Semple, ""Immigrants Find Voting Can Come At a Cost". New York Times, October 15, 2010.
- ^ "Felon Voting Rights". ncsl.org. October 1, 2020. Retrieved Oct 30, 2020.
- ^ "Inaccurate, Costly, and Inefficient: Testify That America'south Voter Registration System Needs an Upgrade" (PDF). The Pew Charitable Trusts. February 2012. Retrieved February 16, 2015.
- ^ "Make It Like shooting fish in a barrel: The Case for Automatic Registration". Democracy. 2013. Retrieved Feb xvi, 2015.
- ^ Raymond E. Wolfinger and; Steven J. Rosenstone (1980). Who Votes?. Yale University Press. pp. 73, 78. ISBN978-0-300-02552-1.
- ^ Frances Trick Piven; Richard A. Cloward (1988). Why Americans don't vote . Random House. ISBN978-0394553962.
- ^ Toby S. James (2012). Elite Statecraft and Election Administration: Bending the Rules of the Game?. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN978-0-230-30842-eight.
- ^ Adam Berinsky (July 2015). "The perverse consequences of balloter reform in the U.s." (PDF). American Politics Research. 33 (4): 471–491. CiteSeerX10.1.1.524.5567. doi:ten.1177/1532673X04269419. S2CID 18424415.
- ^ Adam Berinsky (Feb eight, 2016). "Making Voting Easier Doesn't Increase Turnout". Stanford Social Innovation Review . Retrieved April vii, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e Online Voter Registration
- ^ a b "Texas begins letting people register to vote online when they're updating their driver's licenses". September 24, 2020.
- ^ You can now register to vote online in Alabama
- ^ a b c d e f 1000 h i List of States Adopting Electronic Registration, Online Voter Registration, or Both
- ^ ONLINE VOTER REGISTRATION (OLVR) SYSTEMS IN ARIZONA AND WASHINGTON: EVALUATING USAGE, PUBLIC CONFIDENCE AND IMPLEMENTATION PROCESSES
- ^ California launches online voter registration
- ^ Online Voter Registration
- ^ Voter Registration and Absentee Ballots
- ^ Office of Elections launches online voter registration organisation
- ^ "Idaho launches online voter registration | the Spokesman-Review".
- ^ Online voting registration begins in Illinois
- ^ Voter Registration
- ^ Iowa Residents Tin Register to Vote Online
- ^ Online voter registration comes to Kentucky
- ^ "Maine to let online voter registration in November 2023". July 23, 2021.
- ^ Online Voter Registration
- ^ Massachusetts Launches Online Voting Registration System
- ^ "SOS - Benson announces beginning of online voter registration and availability of eNotary services in Michigan". www.michigan.gov . Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- ^ Editorials: Online voter registration offers multiple advantages | Marker Ritchie/PostBulletin
- ^ Want to register to vote online in Nebraska? Now you can
- ^ Wildstein, David (September 4, 2020). "Online voter registration in N.J. goes live". New Jersey Globe . Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ "New Bailiwick of jersey Section of State - Press Releases - September 8, 2020, NJ Division of Elections".
- ^ Online Voter Registration At present Bachelor in New Mexico!
- ^ NCSBE Printing Release
- ^ Ohio's Online Voter Registration Organisation is At present Live
- ^ a b Online Voter Registration
- ^ Oregon offers online voter registration
- ^ Pennsylvania Launches Online Voter Registration to Increase Efficiency and Offer Convenience
- ^ R.I. secretary of state: Voter registration is easier with new online organisation
- ^ South Carolina Launches Online Voter Registration System
- ^ After A Year In The Works, Online Voter Registration Goes Live In Tennessee
- ^ Online Voter Registration Now Open In Vermont
- ^ Virginia residents tin can now annals to vote online
- ^ The Launch of Online Voter Registration in Wisconsin through MyVote.wi.gov
- ^ "Automatic Voter Registration, a Summary | Brennan Middle for Justice".
- ^ "National Briefing of State Legislatures: Automatic Voter Registration". ncsl.org. April 22, 2019. Retrieved October 7, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Automatic Voter Registration". Brennan Center for Justice. July 24, 2018. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- ^ "Oregon Secretary of Country: Oregon Motor Voter Human action FAQ". sos.Oregon.gov . Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ "Automated Voter Registration". Brennan Heart for Justice. Apr 1, 2016. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ^ "Shumlin signs into police force automatic voter registration". Vermont Business Magazine. April 28, 2016. Retrieved Apr 28, 2016.
- ^ Lieutenant Governor Byron Mallott (March 7, 2016). "Proper Filing Letter" (PDF). Alaska Division of Elections. Retrieved December x, 2016.
- ^ "Unofficial Results - November 8, 2016 Full general Ballot" (PDF). Alaska Sectionalization of Elections. November 23, 2016. Retrieved December ten, 2016.
- ^ "Cuomo Signs Automatic Voter Registration Measure". spectrumlocalnews.com . Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ "Automated Voter Registration". Brennan Center for Justice . Retrieved May 12, 2016.
- ^ "Illinois governor signs automatic voter registration police". Washington Mail. August 28, 2017. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017. Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ PFD Automatic Voter Registration & Updates to Registrations FAQ's
- ^ "DMV voter registration approved by General Assembly".
- ^ "Bill Particular - Delaware General Assembly".
- ^ Automatic Voter Registration Begins at DC DMV on June 26, 2018
- ^ Automatic voter registration at DMV begins in IL
- ^ "Automated Voter Registration | League of Women Voters". www.lwvme.org . Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ Dwyer, Paul. "State lawmakers get update on automatic voter registration". world wide web.wabi.tv . Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ "SOM - Secretary Benson announces modernized voter registration on National Voter Registration Day". www.michigan.gov . Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- ^ Contained, TABITHA MUELLER SHANNON MILLER, JAZMIN OROZCO RODRIGUEZ KRISTYN LEONARD The Nevada. "Nevada voter rolls swell as automatic registration takes effect". Elko Daily Free Press . Retrieved Jan 24, 2020.
- ^ Writer, MICHELLE BRUNETTI POST Staff. "Voter registration now automatic at NJ Motor Vehicle Commission". Press of Atlantic Urban center . Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ a b c "Gov. Lujan Grisham enacts same-day, automated voter registration | Office of the Governor - Michelle Lujan Grisham". Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ "Cuomo Signs Automatic Voter Registration Measure out".
- ^ Oregon Motor Voter Act FAQ
- ^ HB 235 Voter registration; automated voter registration.
- ^ Ponoroff, Christopher (2010). Voter Registration in a Digital Age (PDF). Brennan Heart For Justice. pp. 3–viii.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j m l m north o p q r s t u v w ten y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq Aforementioned Day Voter Registration
- ^ June 11, 2011,Beak to cease aforementioned-day registration approved Portland Printing Herald
- ^ August 14, 2011, Citizens rise up in Maine Archived Nov vii, 2011, at the Wayback Automobile Boston Globe
- ^ Nov 8, 2011, Huff Mail service Politics, Maine Ballot Day Registration Restored Past Voters
- ^ Timpe, Brenden (March fourteen, 2013). "New Study: Higher Voter Turnout Linked to SDR". Demos (U.Southward. think tank). Retrieved May 29, 2013.
- ^ "America Goes to the Polls 2014 - Nonprofit Vote". world wide web.NonprofitVote.org . Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ Pillsbury, George; Johannesen, Julian (March 2015). "America Goes to the Polls 2014" (PDF). world wide web.NonprofitVote.org. Nonprofit VOTE.
- ^ Brians, Craig Leonard; Grofman, Bernard (March 1, 2001). "Election Day Registration's Effect on U.Due south. Voter Turnout". Social Science Quarterly. 82 (one): 170–183. doi:10.1111/0038-4941.00015. ISSN 1540-6237.
- ^ Rhine, Staci L. (January 1, 1996). "An Analysis of the Impact of Registration Factors on Turnout in 1992". Political Behavior. eighteen (2): 171–185. doi:10.1007/BF01498789. JSTOR 586605. S2CID 154760679.
- ^ Ansolabehere, Stephen; Konisky, David M. (December 21, 2006). "The Introduction of Voter Registration and Its Event on Turnout". Political Assay. 14 (1): 83–100. CiteSeerX10.1.1.170.1688. doi:10.1093/pan/mpi034. ISSN 1047-1987.
- ^ Brunt, Barry C.; Catechism, David T.; Mayer, Kenneth R.; Moynihan, Donald P. (Jan 1, 2014). "Election Laws, Mobilization, and Turnout: The Unanticipated Consequences of Election Reform". American Journal of Political Science. 58 (1): 95–109. CiteSeerXx.1.1.644.6582. doi:ten.1111/ajps.12063. ISSN 1540-5907.
- ^ Neiheisel, Jacob R.; Brunt, Barry C. (July 1, 2012). "The Bear upon of Ballot Day Registration on Voter Turnout and Ballot Outcomes". American Politics Research. xl (four): 636–664. doi:10.1177/1532673X11432470. ISSN 1532-673X. S2CID 10525201.
- ^ Highton, Benjamin (September 1, 2004). "Voter Registration and Turnout in the Usa". Perspectives on Politics. 2 (3): 507–515. doi:10.1017/S1537592704040307. ISSN 1541-0986. S2CID 145629037.
- ^ Grumbach, Jacob Thousand.; Hill, Charlotte (2021). "Stone the Registration: Same Day Registration Increases Turnout of Young Voters". The Journal of Politics. doi:10.1086/714776. ISSN 0022-3816.
- ^ "Maine towns back Aye on 1, same-mean solar day voter signup — Politics". Bangor Daily News. October 11, 2011. Retrieved December 17, 2015.
- ^ a b "News Update - Transition to QVF Refresh, Recount Request Deadline Elapses, and More than". Michigan Secretarial assistant of State . Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ a b Reichbach, Matthew (March 27, 2019). "Gov. signs same-twenty-four hour period voter registration beak". The NM Political Report . Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- ^ Millions to the Polls
- ^ FAQ - Voting
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u five west 10 y z aa ab air conditioning ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax Preregistration for Young Voters
- ^ Charles H. Wesley Education Foundation five. Cathy Cox.
- ^ Cox Violated Voter Rights, Judge Declares Archived 2014-08-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "More than cities consider letting 16-year-olds vote in local elections". Washington Postal service. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- ^ "D.C. Council declines to take up bill to lower voting historic period to 16". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- ^ a b 2020 Election Calendar
- ^ VOTER REGISTRATION Process
- ^ Borderline looming to switch party earlier Connecticut primary
- ^ Party amalgamation change deadline approaching
- ^ a b Borderline to change political party amalgamation status
- ^ Primary Elections in Idaho
- ^ Fri is borderline to change party affiliation in Idaho
- ^ a b c Deadlines to change party affiliation in airtight master states
- ^ Deadline nears to change political party affiliation
- ^ a b Borderline to Change Party Amalgamation Alee of 2018 May Primary is Dec. 31
- ^ Deadline to Alter Party Enrollment in Time to Vote in June 12 Primary
- ^ Political party Affiliation in New Hampshire
- ^ June 5, 2018 Deadline to Change Party Affiliation for Voting in the September 11, 2018 State Master Election
- ^ Sectionalisation of Elections Reminds Registered Voters of Upcoming Apr xi Deadline for Change of Party Amalgamation Declaration Forms for Primary Election to be Filed with County Commissioners of Registration
- ^ New York Consolidated Laws, Election Constabulary - ELN § five-304. Enrollment; modify of enrollment or new enrollment by previously registered voters
- ^ "Yous Take Until February 14th To Modify Your Political party Registration For The 2020 Presidential Main". Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- ^ Often Asked Questions
- ^ R.I. voters have until June fourteen to switch party affiliations earlier Sept. 12 primary
- ^ a b Welcome to the FAQs
How Many People Register To Be Democrat,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voter_registration_in_the_United_States
Posted by: moranineved85.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Many People Register To Be Democrat"
Post a Comment